Author: Ali Hasanbeigi, Ph.D.
According to IPCC, the industry sector accounts for about a quarter of the world’s total anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (after allocating electricity-related emission to end use sectors). The steel, chemical, and cement industry account for around 65% of total manufacturing GHG emissions.
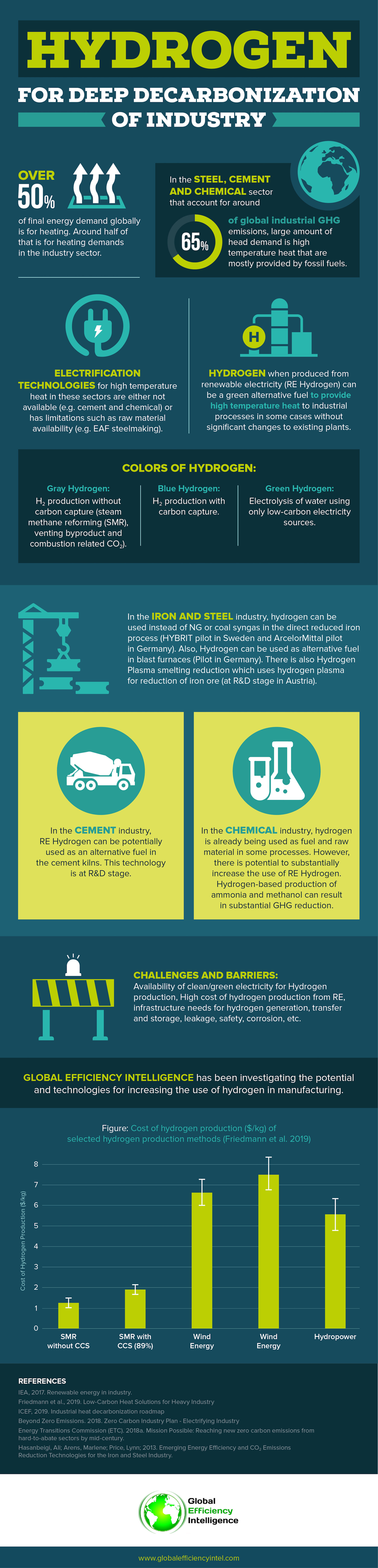
Over 50% of final energy demand globally is for heating. Around half of that is for heating demands in the industry sector. Unlike transportation and building sector, the industry sector is more complex and it is more difficult to electrify its head demand using renewable energy sources. It is especially challenging to electrify high temperature head demand for energy-intensive sectors such as the cement and chemical industry. Figure below shows the temperature requirements of key industrial processes and the temperature limits provided by some options for low-carbon heat source replacements.
Figure. Temperature requirements of key industrial process and the temperature limits provided by some options for low-carbon heat source replacements (Friedmann et al. 2019, ICEF 2019)
Hydrogen when produced from renewable electricity (RE Hydrogen) can be a green alternative fuel to provide high temperature heat to industrial processes in some cases without significant changes to existing plants. Biomass is another option, but has challenges such as local availability and sustainability of its supply sources.
The infographic below highlights some general aspects of Hydrogen use as an alternative fuel or raw materials in the industry sector. There is a substantial need for more research and analysis on the potential use of hydrogen in different industry subsectors and technologies RD&D needs and challenges.
Don't forget to Follow us on LinkedIn , Facebook and Twitter to get the latest about our new blog posts, projects, and publications.