Low-Carbon Thermal Energy Technologies for The Textile Industry
The textile and apparel industry generates approximately 2% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The demand for textiles and apparel is expected to grow, highlighting an urgent need for strategies to mitigate the industry’s environmental and climate impacts.
This report, commissioned by the Apparel Impact Institute (Aii) and authored by Global Efficiency Intelligence, explores the feasibility, challenges, and potential of transitioning to low-carbon thermal energy sources and technologies in the textile industry, focusing on sustainable biomass, solar thermal, electrification technologies, and natural gas (a potential transition fuel). The electrification technologies include electric boilers, industrial heat pumps, and thermal energy storage systems. Overall, six alternative energy sources and technologies are included in this report.
We conducted a readiness assessment for adopting low-carbon energy sources and technologies among the world’s leading textile-producing countries in the near term. For each energy source and technology, multiple criteria were assessed, such as the availability of resources domestically, the average carbon intensity of fuel used in the industry, climate policy strength, technology availability in each country, and other considerations. The results divide the countries by readiness to adopt each technology into categories of most ready, moderately ready, and less ready.
We also evaluated each energy source and technology against several indicators: capital and operational expenditures, energy costs, technological maturity, market growth outlook, thermal efficiency, CO2 emissions, and other environmental risks. The cross-technology comparison highlights the overall maturity and applicability of each energy source and technology for the textile industry. Biomass, despite its potential for carbon neutrality, faces challenges such as deforestation and land use change. Natural gas, while mature, grapples with price volatility and climate and environmental risks, notably methane leakage that can eliminate its climate benefits compared to coal. Solar thermal technologies, although able to provide zero-carbon heat, face challenges for textile applications because of the industry’s significant steam and heat requirements above 100°C. They also require significant space and investment and are highly dependent on the location of the plant. Electrification technologies, when tied to renewable electricity, have the best potential to decarbonize the textile industry. However, the scarcity of the required renewable energy at a reasonable price and competition from other industrial sectors for this resource is a challenge in the near term, especially in some low- and middle-income countries.
We then provide a detailed summary of each energy source and technology, including a description of how the technology works, strengths and opportunities as a low-carbon solution for the textile industry, challenges to adoption, supply and infrastructure considerations, and costs. A case study is also provided for each energy source and technology.
Electrification emerges as a highly efficient solution for low-carbon thermal energy, requiring minimal onsite infrastructure adjustments. Widespread adoption is constrained by energy costs, the existing carbon intensity of electricity grids in some countries, and supply of renewable electricity in key textile-producing countries, but in some cases electrification can be economically competitive with conventional technologies in the near- to medium-term. In addition, as in other industrial sectors, renewable electricity can be purchased at textile plants via Power Purchase Agreements (PPA), delivering decarbonization via electrification immediately.
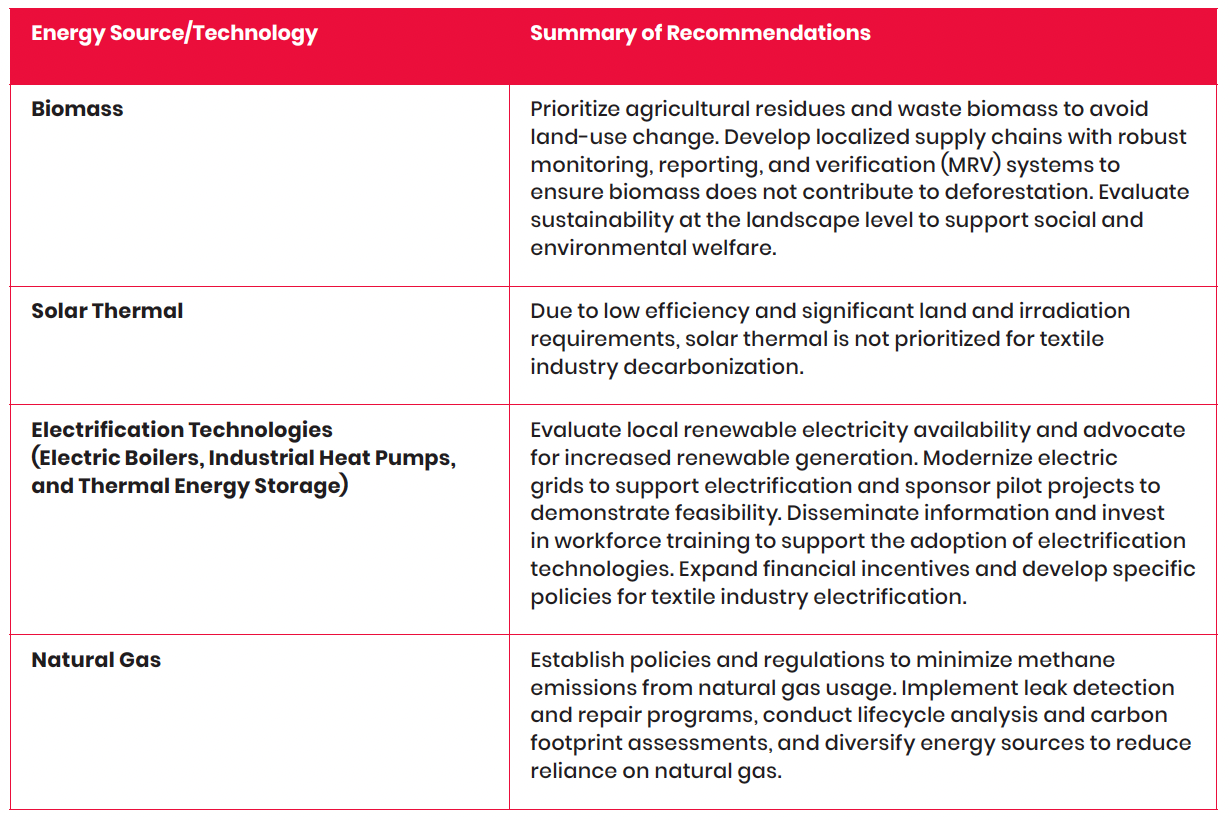
A series of tailored actions and recommendations for apparel companies and textile suppliers emerged from the analysis, aimed at advancing the adoption of low-carbon energy sources and electrification technologies in the textile industry (Table 1).
Table 1. Summary of Recommendations for Advancing Low-Carbon Thermal Energy Technologies in the Textile Industry
This report serves as a guide for stakeholders in the textile and apparel industry, aiming to navigate the complex terrain of decarbonization. By evaluating and integrating low-carbon energy sources and technologies for process heating, the textile industry can significantly reduce its carbon footprint, contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
To read the full report and see complete results and analysis of this new study, Download the full report from the link above.
This is the first of a two-report series. Our next report, to be published in November 2024, will provide a detailed Low Carbon Thermal Energy Roadmap for the Textile Industry in five major textile-producing countries. Stay tuned!
Interested in information and decarbonization studies on the global textile and apparel industry? Check out our list of textile industry publications on the Textile Sustainability Hub.